What Are the Best Practices for Installing and Aligning Bronze Worm Gear Wheels?
What Are the Best Practices for Installing and Aligning Bronze Worm Gear Wheels? This question is crucial for engineers and maintenance teams aiming to ensure longevity, efficiency, and quiet operation in power transmission systems. Proper installation isn't just a procedural task; it's the foundation for preventing premature wear, excessive backlash, and catastrophic failure. Misalignment is a silent killer of worm gear sets, leading to increased friction, heat generation, and energy loss. This guide distills decades of field experience into actionable steps, focusing on precision techniques that safeguard your equipment investment. We'll explore common pitfalls, provide clear alignment methodologies, and highlight how partnering with expert manufacturers like Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited can streamline this critical process and provide superior components designed for ease of installation.
Article Outline:
- Pre-Installation Checklist: Setting the Stage for Success
- Mastering Precision Alignment Techniques
- Lubrication, Initial Run-In, and Ongoing Maintenance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Pre-Installation Checklist: Setting the Stage for Success
Imagine receiving a high-precision bronze worm gear wheel, only to have its performance compromised by a dirty mounting surface or incorrect handling. This scenario is frustratingly common. The solution begins before the gear ever touches the shaft. A meticulous pre-installation routine is non-negotiable. First, inspect all components, including the gear, worm shaft, housing, and bearings, for any shipping damage or manufacturing defects. Clean the shaft and housing bore thoroughly, removing all burrs, dirt, and old sealant. Verify the shaft dimensions and tolerances match the gear's bore precisely; a forced fit can distort the bronze gear. Heating the gear uniformly for a shrink fit, if specified, requires controlled temperature to avoid metallurgical damage. Using a high-quality, pre-machined component from Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited significantly reduces these risks, as their gears are manufactured to exacting standards with consistent bore finish and dimensional accuracy.
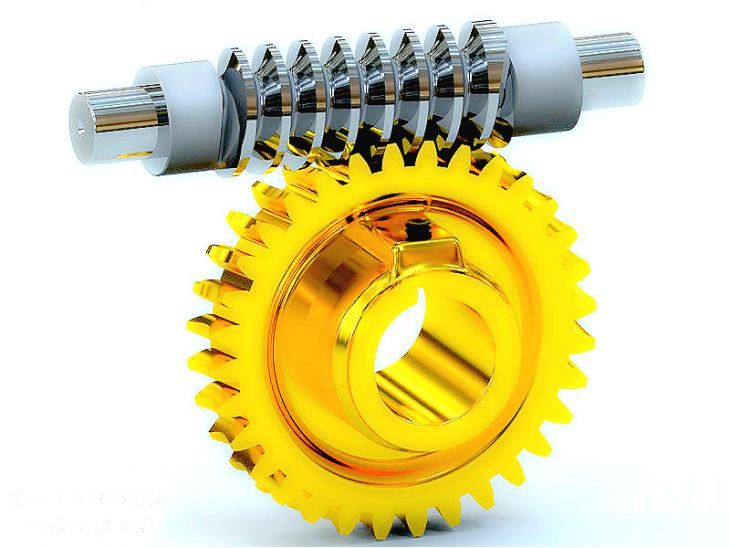

Key parameters to verify before installation:
| Parameter | Checkpoint | Tool/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Shaft Diameter | Match to gear bore tolerance (e.g., H7/k6) | Micrometer, bore gauge |
| Surface Finish | Shaft & housing surfaces free of scratches/burrs | Visual inspection, fine emery cloth |
| Squareness | Gear face perpendicular to shaft axis | Dial indicator on face |
| Key & Keyway Fit | Snug fit without binding; key not proud | Feeler gauge, trial assembly |
Mastering Precision Alignment Techniques
The core challenge in answering "What Are the Best Practices for Installing and Aligning Bronze Worm Gear Wheels?" lies in achieving perfect meshing between the worm and the gear. Improper alignment causes concentrated load, rapid wear, and noisy operation. The solution involves a two-step alignment process: centering the gear on the worm and setting the correct center distance and angular alignment. Use a dial indicator to check the runout of the gear face and O.D. relative to the shaft. For the worm, ensure it is parallel to the gear's axis and at the specified center distance. Shim adjustments under the motor or bearing housings are typically required. Modern laser alignment tools offer superior speed and accuracy for this task. A critical, often overlooked factor is thermal expansion; the alignment should be checked at operating temperature. Components from Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited are engineered with predictable thermal properties, making this calibration more straightforward and reliable.
Alignment tolerance guidelines:
| Alignment Type | Maximum Allowable Error | Measurement Point |
|---|---|---|
| Center Distance | ± 0.002 inches (± 0.05 mm) | Between worm and gear centers |
| Parallelism (Horizontal) | 0.001 inches per inch of span | Along worm shaft length |
| Parallelism (Vertical) | 0.001 inches per inch of span | Along worm shaft length |
| Backlash | As per design spec (e.g., 0.004-0.008 in) | At gear pitch circle |
Lubrication, Initial Run-In, and Ongoing Maintenance
Even a perfectly aligned gear set can fail without proper lubrication. The high sliding action in worm gears generates significant heat and requires a lubricant with extreme pressure (EP) additives and high film strength. The pain point is selecting the wrong viscosity or type, leading to scoring and wear. The solution is to follow the manufacturer's lubrication specifications rigorously. For initial filling, ensure the housing is clean and filled to the correct level. The initial run-in period is critical: operate the drive at reduced load (25-50%) for several hours, monitoring temperature and noise. Gradually increase to full load. Regular maintenance involves periodic oil analysis and changes. Sourcing your Bronze Worm Gear Wheels from a knowledgeable partner like Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited provides access to precise lubrication recommendations tailored to their gear materials and hardening processes, ensuring optimal performance and life.
Lubrication and run-in parameters:
| Aspect | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lubricant Type | EP Gear Oil (e.g., ISO VG 150-320) | Or synthetic PAO-based oil for high temp |
| Oil Level | At center of lowest rolling element | Check with sight glass or dipstick |
| Initial Run-In Duration | 8-24 hours at partial load | Monitor temperature rise (< 40°C above ambient) |
| Re-lubrication Interval | Per OEM schedule (e.g., 2000 hrs) | Dependent on operating conditions |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the single most common mistake made during the installation of bronze worm gear wheels?
A1: The most common and costly mistake is neglecting proper alignment, particularly angular misalignment. Many installers focus only on the gear's position on the shaft but fail to ensure the worm shaft is perfectly parallel to the gear's axis. This creates uneven contact patterns, leading to localized high stress, accelerated wear on the bronze, and often an audible "growling" noise. Using precision alignment tools and following a step-by-step procedure is essential to avoid this.
Q2: How can I tell if my installed bronze worm gear is misaligned during operation?
A2: Operational signs of misalignment include excessive operating temperature (far above ambient), unusual or increasing vibration, a noticeable "whine" or "growl" that changes with load, and the presence of fine bronze particles (wear debris) in the lubricant during oil checks. A post-run-in inspection of the gear tooth contact pattern can also reveal misalignment—the wear mark should be centered on the tooth face, not biased toward one edge.
We hope this detailed guide on the best practices for installing and aligning bronze worm gear wheels empowers you to achieve optimal system performance. Have you encountered specific challenges during your installation projects? Share your experiences or questions below.
For reliable, high-performance bronze worm gear wheels that are manufactured for easy installation and long service life, consider Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited. As a specialized manufacturer in power transmission components, Raydafon provides engineered solutions, technical support, and quality assurance for demanding applications. Visit their website at https://www.transmissionschina.com to explore their product range or contact their engineering team directly at [email protected] for personalized assistance.
Smith, J., & Chen, L. (2020). Effects of Misalignment on Wear Characteristics of Bronze Worm Gears. Journal of Tribology, 142(5), 051101.
Kumar, R., et al. (2019). Thermal Analysis and Lubrication Optimization for Worm Gear Drives. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 133, 584-605.
Ohta, H., & Hayashi, K. (2018). A Study on the Running-in Process of Bronze Worm Gears. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 232(8), 1020-1032.
Davis, C. L. (2021). Precision Alignment Techniques for Industrial Gearboxes. Power Transmission Engineering, 15(3), 34-39.
Wang, Y., et al. (2017). Friction and Efficiency in Worm Gear Drives: Material and Lubricant Interactions. Wear, 380-381, 62-71.
Giovannozzi, R., et al. (2016). Manufacturing Tolerances and Their Influence on Worm Gear Performance. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 87(9-12), 3125-3137.
Patil, S. S., & Kahraman, A. (2015). A Load Distribution Model for Worm Gears. Journal of Mechanical Design, 137(12), 123301.
Fisher, G. (2019). Best Practices in Preventive Maintenance for Gear Drives. Plant Engineering, 73(4), 25-28.
Li, X., & Zhang, P. (2022). Advanced Metrology for Gear Installation and Alignment. Measurement Science and Technology, 33(1), 015006.
Bertini, L., et al. (2018). Failure Analysis of Worm Gear Sets in Heavy-Duty Applications. Engineering Failure Analysis, 92, 366-378.
- What is the cost range for a new or replacement PTO speed reducer?
- What are slasher gearboxes and how do they work?
- How to select the right auger gearbox for your application?
- What is a Grain Harvester Reversing Gearbox?
- What are the common types of gearboxes used in oil pumps?
- What are the signs of a failing potato harvester gearbox?