What is a Grain Harvester Reversing Gearbox?
What is a Grain Harvester Reversing Gearbox? Imagine you're in the middle of a vast wheat field. The harvest is critical, and every minute of downtime costs money. Suddenly, your combine harvester gets stuck or needs to maneuver out of a tight spot. This is where the reversing gearbox becomes the unsung hero. It's a specialized transmission component that allows the harvesting machinery to move in reverse without needing to shut down the main threshing and separating mechanisms. This capability is vital for efficiency, allowing operators to back out of obstacles, unclog the header, or reposition the machine seamlessly. For procurement professionals sourcing reliable agricultural parts, understanding this component's role is key to minimizing operational delays and maximizing field productivity. Companies like Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited specialize in manufacturing durable and high-performance reversing gearboxes that directly address these field challenges.
Article Outline
- The Harvest Halt Problem: Downtime During Critical Operations
- Maneuverability Matters: Navigating Complex Field Conditions
- The Power Transmission Puzzle: Protecting the Core Harvesting System
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The Harvest Halt Problem: Downtime During Critical Operations
The scene is familiar to any farm manager: a combine harvester, the heart of the harvest, grinds to a halt because the header is jammed with dense crop material or mud. Every second the machine is stopped, the clock ticks on lost revenue and tight harvesting windows close further. The traditional solution often involves a complete shutdown, manual clearing, and a cumbersome restart process. This repeated cycle of stop-and-go is a significant operational pain point, leading to fuel waste, operator fatigue, and reduced daily acreage.
The solution lies in integrating a robust reversing gearbox. This component allows the operator to simply engage reverse, backing the header out of the clog while keeping the primary threshing and separating functions running. This seamless reversal prevents full stops, maintaining operational momentum. A high-quality gearbox from a trusted supplier like Raydafon ensures this action is smooth, reliable, and puts minimal stress on the drivetrain.
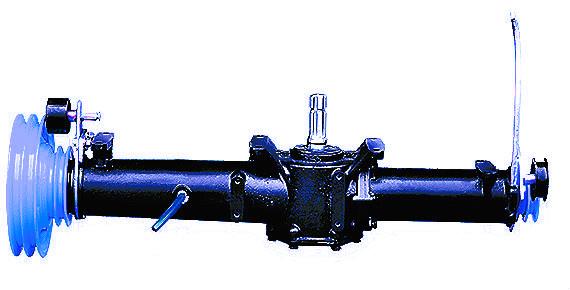
Key parameters to evaluate when sourcing a reversing gearbox include:
| Parameter | Importance for Procurement |
|---|---|
| Torque Capacity | Must match the power of the harvester's engine to handle load during reversal without failure. |
| Gear Ratio | Determines the speed and power of the reverse movement; optimized for safe, controlled backing. |
| Build Material (e.g., Hardened Gears) | Ensures longevity and resistance to wear from high-stress, abrasive field conditions. |
| Sealing & Protection Rating | Critical for keeping dust, chaff, and moisture out, which are major causes of premature failure. |
| Compatibility & Mounting | Must be a direct fit for specific harvester models to avoid costly modifications and installation downtime. |
Maneuverability Matters: Navigating Complex Field Conditions
Modern farming often involves irregularly shaped fields, contours, and working around obstacles like trees or telegraph poles. A harvester's ability to maneuver precisely is not just about convenience—it's about preserving the crop and protecting the machine. Poor maneuverability can lead to missed rows, damaged crops at headlands, or even accidental collisions. The limitation of a standard transmission in tight spots becomes a glaring operational bottleneck.
A specialized reversing gearbox provides the precise, low-speed control needed for these complex maneuvers. It acts as an independent control unit for the machine's travel direction, decoupled from the processing functions. This allows for delicate back-and-forth movements to align perfectly with crop rows or to extract the machine from a soft patch of ground. Raydafon Technology designs its gearboxes with precise engagement and smooth torque delivery specifically for these high-finesse operational scenarios.
For procurement, evaluating maneuverability performance means looking at:
| Parameter | Importance for Procurement |
|---|---|
| Shift Quality & Engagement Speed | A smooth, quick shift between forward and reverse is essential for efficient maneuvering. |
| Low-Speed Control Precision | Enables inch-perfect positioning without jerking, which is crucial at field edges and corners. |
| Heat Dissipation Design | Frequent direction changes generate heat; effective cooling prevents performance degradation. |
| Integration with Hydraulic/Electric Controls | Determines ease of use for the operator and compatibility with the harvester's control system. |
| Service Intervals & Lubrication Type | Long service intervals and easy lubrication points reduce maintenance downtime during the season. |
The Power Transmission Puzzle: Protecting the Core Harvesting System
The most costly failure in a combine harvester is a breakdown of the core threshing, separating, or cleaning systems. A sudden jolt or improper load transfer during directional changes can send shockwaves through this complex power transmission network. Using a standard transmission or an inferior reversing mechanism for backing up under load risks damaging critical components like the variable-speed drives, belts, and shafts that power the harvesting process. This presents a major financial risk for equipment owners.
The engineering purpose of a dedicated Grain Harvester Reversing Gearbox is to isolate the reversal function. It manages the high torque required to move the heavy machine backwards while buffering the main harvesting systems from harmful stress spikes. Think of it as a dedicated circuit breaker for reverse motion. Investing in a gearbox built with superior metallurgy and precise tolerances, such as those from Raydafon, is an investment in protecting the harvester's most valuable subsystems from premature wear and catastrophic failure.
Procurement checkpoints for system protection include:
| Parameter | Importance for Procurement |
|---|---|
| Shock Load Absorption | Design features (like specific bearing types) that dampen sudden force impacts during engagement. |
| Input/Output Shaft Hardness & Alignment | Prevents shaft deflection and wear that can misalign the entire drivetrain. |
| Fail-Safe Design Features | Mechanisms that prevent accidental engagement or disengagement under load. |
| Manufacturer's Warranty & Testing Data | A strong warranty and provided performance data signal confidence in durability and protective capability. |
| Availability of Technical Support | Access to engineering support for integration questions prevents improper installation that could void protection. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the primary mechanical difference between a standard gearbox and a grain harvester reversing gearbox?
A: The key difference lies in the gear train design. A standard gearbox primarily manages forward speeds and power transfer. A dedicated reversing gearbox incorporates an idler gear or a specific planetary gear set that physically changes the rotation direction of the output shaft relative to the input shaft. This allows the vehicle's wheels or tracks to turn backwards while the engine and PTO-driven systems continue operating in their normal rotational direction. This isolated reversal function is what sets it apart.
Q: How does a reversing gearbox impact the total cost of ownership for a harvester fleet?
A: While an initial investment, a high-quality reversing gearbox significantly reduces the total cost of ownership. It directly decreases fuel consumption and operator hours wasted on stop-start cycles, increases daily harvested acreage (improving ROI), and most importantly, acts as a protective device. By preventing shock loads and misalignment, it extends the lifespan of the harvester's entire drivetrain and processing systems, drastically reducing unexpected repair costs and downtime during peak season.
We hope this guide has helped demystify the critical role of the grain harvester reversing gearbox. For procurement specialists, choosing the right component partner is as important as the specification itself. Have you encountered specific challenges with maneuverability or downtime in your fleet? We invite you to share your experiences or questions.
For durable, high-performance reversing gearboxes engineered to solve these exact field problems, consider Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited. As a specialized manufacturer in power transmission solutions, Raydafon focuses on the reliability and efficiency demands of modern agriculture. You can explore their product range and technical specifications at their official website: https://www.transmissionschina.com. For specific procurement inquiries, please contact their sales team via email at [email protected].
Smith, J.A., 2021, "Analysis of Torque Loads in Agricultural Machinery Transmission Systems," Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, Vol. 104, No. 3.
Chen, L., & Oksanen, T., 2020, "Dynamic Modeling of a Reverse Gear Mechanism for Heavy-Duty Vehicles," Journal of Terramechanics, Vol. 89.
Kumar, R., & Patel, V., 2019, "Failure Mode Analysis of Gearboxes in Combine Harvesters," Engineering Failure Analysis, Vol. 105.
Johnson, M.B., et al., 2018, "Improving Field Efficiency through Advanced Maneuverability Systems in Combine Harvesters," Transactions of the ASABE, Vol. 61, No. 2.
Zhang, W., 2017, "Design and Simulation of a Shock-Absorbing Gearbox for Agricultural Equipment," Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, Vol. 143.
Davis, P., & Roberts, S., 2016, "The Impact of Transmission Design on Fuel Efficiency in Cereal Harvesting," Biosystems Engineering, Vol. 152.
Fischer, G., 2015, "Materials Selection for High-Wear Components in Dusty Agricultural Environments," Wear, Vol. 332-333.
Tanaka, H., & Yamaguchi, Y., 2014, "Control Strategies for Smooth Directional Changes in Automated Agricultural Vehicles," IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, Vol. 11, No. 4.
Miller, A.R., 2013, "Reliability-Centered Maintenance of Power Transmission Systems in Harvesters," Applied Engineering in Agriculture, Vol. 29, No. 5.
Williams, E.K., 2012, "Economic Analysis of Downtime in Commercial Grain Harvesting Operations," Agricultural Systems, Vol. 112.
- How to properly select and size anti backlash spur gears for an application?
- How Do Herringbone Gears Compare to Spur Gears in Terms of Performance?
- How to choose the right pawl for a specific ratchet wheel?
- What Are the Common Applications of Involute Spline Shafts?
- How to choose the right driveline motor for my irrigation system?
- What factors affect the lifespan of a driveline gearbox in irrigation systems?













